



Next: Symbols
Up: JFFS3design
Previous: Issues/ideas/to be done
Contents
Definitions
- Access Control Lists, ACL - a modern mechanism to control
accesses to files which provides much more flexibility that the standard Unix
mechanism of owner/group/others permissions, see [7] for more
details.
- Acl - an object in the tree containing inode's ACL. Refer to
section 4.1 for more information.
- Acl key - acl object's key.
- Acl node - a leaf node containing an acl object.
- Anchor eraseblock, anchor area - the second and the third
good eraseblocks of the JFFS3 partition which are reserved for the
superblock management. See section 6.1 for more details.
- Attr-data - an object in the tree where inode's attributes are
stored (standard Unix attributes like creation time, owner ID, etc and other
attributes like the type of compression, etc). Refer to
section 4.1 for more information.
- Attr-data key - attr-data object's key.
- Attr-data node - a leaf node containing an attr-data
object.
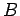 -tree - a balanced search tree where each node has many
children. See section 3.3.
-tree - a balanced search tree where each node has many
children. See section 3.3.
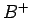 -tree - a
-tree - a 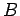 -tree where no data is stored in
non-leaf nodes but instead, is stored only in leaf nodes.
-tree where no data is stored in
non-leaf nodes but instead, is stored only in leaf nodes.
- Branch node - any node that is not leaf, not twig and not root.
- Branching factor - the branching factor of the
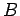 -tree is the
number of children of a node.
-tree is the
number of children of a node.
- Chain eraseblock - an eraseblock containing references to other
chain eraseblocks or to the super eraseblock. Chain eraseblocks facilitate
quick SB searching and are the part of the JFFS3 superblock management scheme
(see section 6.1). The main reason why chain eraseblocks are
needed is the need to provide good flash wear-levelling.
- Clean eraseblock - an eraseblock which contains no garbage, only
valid information.
- Data area - the whole JFFS3 partition excluding the static
superblock and anchor eraseblocks.
- Data key - data object's key.
- Data node - a leaf node with file's data.
- Directory entry, direntry - basically an association between
the name and the inode number.
- Direntry key - direntry object's key.
- Direntry node - a leaf node containing a direntry object.
- Dirt, dirty space - information on flash which is not valid due
to out-of-place updates or objects deletion. It is the aim if the
Garbage Collector to reclaim the space occupied by dirt.
- Dirty eraseblock - an eraseblock which contains some dirt along
with valid nodes.
- Dirty sector - a sector which contains dirt.
- Erasable block, eraseblock - the minimal erasable unit of the
flash chip from the JFFS3's viewpoint.
- Extended attributes, xattr - an association between names and
data for files and directories. See attr(5) Linux manual pages for more
information.
- Fanout - the same as branching factor.
- Free eraseblock - an erased eraseblock (contains only
0xFF words).
- Garbage - the same as dirt.
- Garbage Collector - a part of any Flash File System which
is responsible for recycling dirty space and producing free eraseblocks.
- Indexing information, index - data structures which do not
contain any file system data (files, directories, extended attributes, etc) but
instead, keep track of this data. For example, indexing information allows to
quickly find all the directory entries for any specified directory. In case of
the FAT file system, the File Allocation Table is may be treated as the index,
in case of the ext2 file system the inode table, the bitmap and the set of
direct, indirect, doubly indirect and triply indirect pointers may be
considered as the index. In JFFS3, the index is comprised by the indexing
nodes. See section 3.4 for more information.
- Indexing eraseblock - an eraseblock which contains indexing
nodes.
- Indexing node - a non-leaf node. Indexing nodes have
fixed size (one sector) and contain only keys and links.
- In-place updates, in-place writes - a method of updating
on-media data when the update is written to the physical position where
the data resides (in opposite to out-of-place updates).
- Journal - contains recent JFFS3 changes and all the file system
updates first go to the journal. The purpose of the Journal is to accumulate a
bunch of JFFS3 file system changes and to postpone updating the index. See
section 3.6 for more information.
- Journal commit - the process of re-building the indexing
information for the data which is in the journal. After the journal has been
committed the journal eraseblocks become just leaf eraseblocks.
- Journal eraseblock - an eraseblock containing the journal data.
- Journal tree - an in-memory tree referring Journal nodes
which were not committed so far. When JFFS3 reads, it first looks up the
journal tree to find out whether the searched information is there. See
section 3.6 for more details.
- Key - an identifier of objects in the tree.
- Key type - an unique identifier of the key type. There are
6 key types in JFFS3 (see section 4.3).
- Leaf eraseblock - an eraseblock containing leaf nodes.
- Leaf node - any node from the leaf level of the tree (level 0).
Leaf nodes contain only data and do not further refer other nodes. For more
information see section 3.4.
- NAND page - a basic input output unit of NAND flash chips. ECC
is calculated on the per-NAND page basis. See any NAND flash manual for
more details, e.g., 10.
- Node - a pile of the tree (the tree consists of nodes) as well
as the container for file system data. There are different types of nodes in
JFFS3. For more information see section 3.4.
- Obsolete nodes/data/sectors - the same as dirty nodes,
data or sectors.
- Out-of-place updates, out-of-place writes - a sort of data
updates when the update is not written to the same physical position, but
instead, is written to some other place and the previous contents is treated as
garbage afterwords. Opposite to in-place updates.
- RAM page - an unit of memory management in Virtual
Memory Management subsystem of most modern operating systems (including Linux).
See [9] for more information.
- Sector - the smallest writable unit of the flash chip
from JFFS3's viewpoint. May be equivalent to the minimal physical input/output
unit (like in case of NAND flashes) or larger (like in case of NOR flashes).
- Shared acl - an acl object which is shared by many inodes for
optimization purposes. Refer to section 4.1 for more
information.
- Static eraseblock - the fist good erasable block of the JFFS3
partition where the file system static data is stored. JFFS3 may
only read it and it is created/changed by external formatting tools.
- Superblock - a data structure which describes the whole
JFFS3 file system. Only dynamic data is stored in the superblock, all the
static data is kept in the static superblock. There is a comprehensive
superblock management scheme in JFFS3, see section 6.1.
- Super eraseblock - an eraseblock where the superblock is kept.
See section 6.1 details.
- Target eraseblock - the eraseblock which is currently being
processed by the Garbage Collector, i.e., nodes are moved from the target
eraseblock and it is erased afterwords.
- Quota - a mechanism which allows to assign different limits on
the file system (e.g., restrict users in the number of files they may create or
in the amount of space they may consume, etc). See [8] for more
details about quota support in Linux.
- Tree - the main entity JFFS3 design revolves about. The JFFS3
tree is a wandering
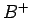 -tree where all the file system stuff (files,
directories, extended attributes, etc) is stored.
-tree where all the file system stuff (files,
directories, extended attributes, etc) is stored.
- Twig nodes - nodes which reside one level upper then leaf nodes
(level 1).
- Valid nodes - nodes which contain actual information,
non-obsolete nodes.
- Wandering tree - a method of updating trees when there is no
possibility to perform in-place updates. The JFFS3 tree is a wandering
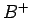 -tree. See section 3.2 for more information.
-tree. See section 3.2 for more information.
- Xattr - a widely used contracted form for extended
attributes.
- Xattr-data - an object in the tree containing the data of an
extended attribute.
- xattr-data key - xattr-data object's key.
- Xattr-data node - a leaf node containing an attr-data
object.
- Xattr ID - an unique identifier of an extended attribute. Refer to
section 4.1 for more information.
- Xentry - an object in the tree which stores the association
between the name of an extended attribute and its xattr ID. Refer to
section 4.1 for more information.
- Xentry key - xentry object's key.
- Xentry node - a leaf node containing a xentry object.




Next: Symbols
Up: JFFS3design
Previous: Issues/ideas/to be done
Contents
Thomas Gleixner
2006-06-23